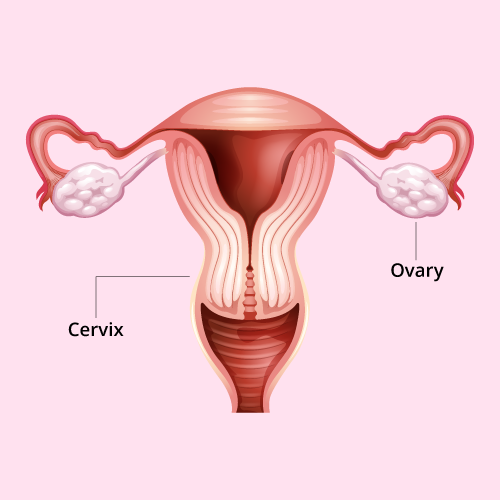
What is Ovarian Cancer
Early-stage ovarian cancer, in which the disease is confined to the ovary, is more likely (about 90-95%) to be treated successfully. However, early ovarian cancer is not easy to detect.
Unfortunately, Ovarian cancer often goes undetected until it has spread within the pelvis and abdomen. At this late stage, ovarian cancer is more difficult to treat and is frequently fatal.
Incidence
- Ovarian cancer is the fifth-leading cause of cancer death in women. Overall, it makes up about 3% of all cancers in women.
- Older women are at higher risk of developing ovarian cancer. More number of cases occur in women who are over 60 years of age.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of Ovarian cancer may include, If the below signs/ symptoms persist, one should consult a doctor.

Swollen abdomen or bloating (due to build-up of fluids produced bytumor)

Lower abdominal and leg pain

Discomfort in the pelvis area

Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation

Quickly feeling full when eating

Sudden weight gain or loss

Nausea/indigestion
Unusual bleeding or discharge from the vagina
Risk Factor
Certain factors were identified that are associated with an increased risk of Ovarian cancer:

Older Age
Ovarian cancer can occur at any age butmore common in women above 60 years.

Family History
People with more affected close relatives have an increased risk.

Personal History
Previous personal history of breast, uterine, or colorectal cancer.

Age of menstruation and menopause
Beginning menstruation at an early age or starting menopause at a later age, or both, may increase the risk of ovarian cancer
Diagnosis
PELVIC EXAMINATION
-
Examination of the body to check general signs of health.During a pelvic exam, doctor visually examines external genitalia, vagina and cervix and inserts gloved fingers into your vagina and simultaneously presses a hand on your abdomen in order to palpate pelvic organs.
IMAGING TESTS
-
Tests, such as ultrasound or CT scans of abdomen and pelvis, may help determine the size, shape and structure of the ovaries.
-
PELVIC ULTRASOUND
-
LAPAROSCOPY
-
LAPAROTOMY
-
BLOOD TESTS
Stages of Ovarian cancer
-
0Cancer is confined to ovary or fallopian tube
-
1Growth of the cancer involves one or both the ovaries with pelvic extension.
-
2Cancer has spread beyond the pelvis
-
3Cancer is widely spread throughout the body
